In constant struggle for the regulation of cannabis, mainly in the medicinal field.
08-06-2018 10:30:03 - Updated: 8 June, 2018
If we start from our conventional tap water we have to take into account the hardness of the water.
Regarding the hardness of the water, we can find water of temporary hardness and permanent hardness, I explain what it is:
-Temporary water hardness: This is due to calcium bicarbonates. It’s temporary because we can easily remove it by heating the water, chemically reacting to the bicarbonate to convert it into CO2….I know what you’re thinking
…Is it the same CO2 as the one we use to boost plant growth? Yes, it is the same, although the amount that comes from bicarbonates is minimal to have any effect on plants…. and… is the same with which extractions are made to develop some of the products of CBD?
Yes, it is the same, although many kilos of CO2 are used for CO2 extractions. In another post we will tell you how the industry uses CO2 to make marijuana oil.
-Permanent water hardness: On the other hand, we have what we call permanent water hardness. It is insoluble matter that cannot be removed by heating, and is mainly due to insoluble sulphates and chlorides. These are the impurities that we can only remove with reverse osmosis filters.
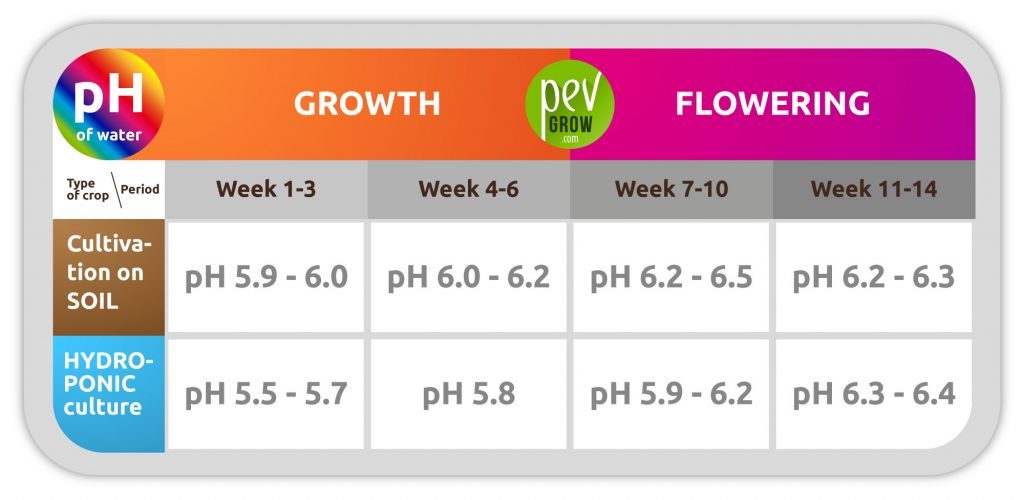
Hard water generally raises the pH of irrigation water and is very harmful to our substrate and plants, as at pH levels above 6.5 plants begin to lose power to absorb nutrients
⭐ Measuring water quality: PH and EC
You can measure the pH with indicator paper, although I recommend a good digital pH meter, which also allows you to measure the level of salts in the water.
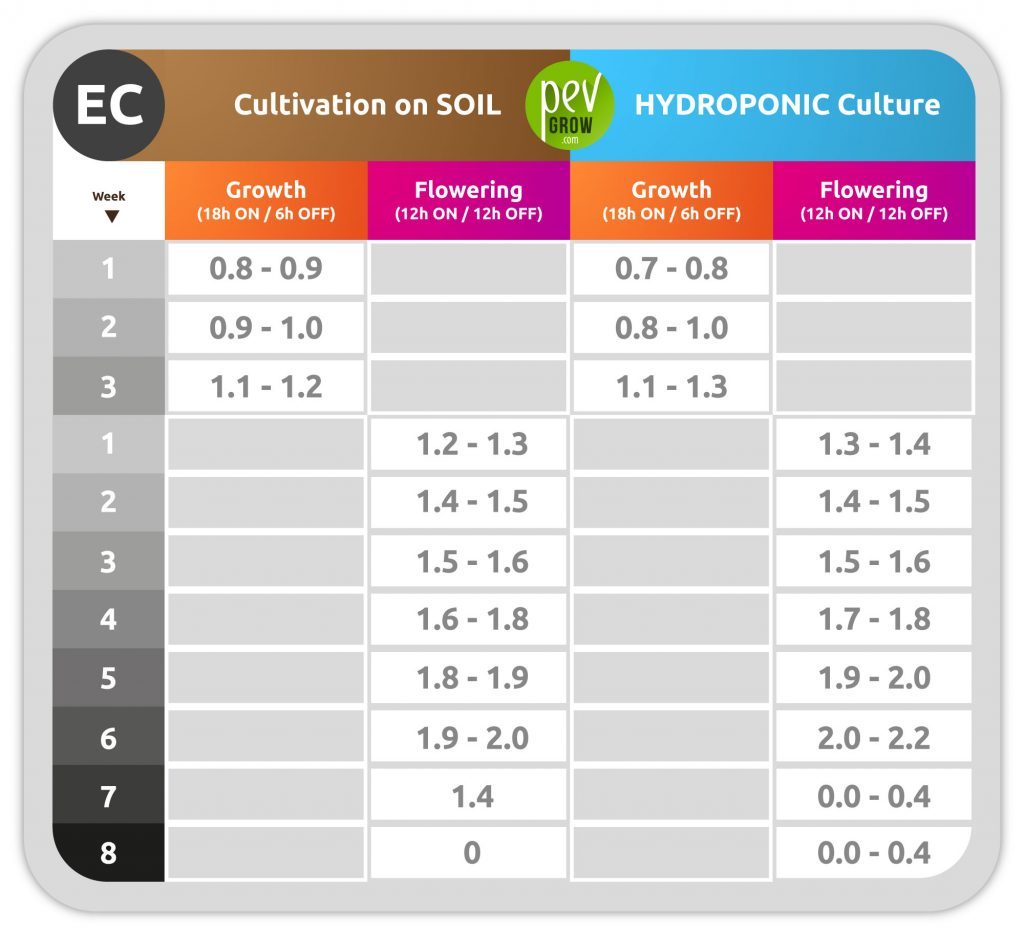
The level of salts in the water is measured with electrical electroconductivity or EC, giving values for osmosis water of between 200 and 500 micro Siemens/cm (micro Siemens per centimetre), we can say that your irrigation water is suitable for your plants. These values will increase as you add different doses of fertilizer.
It is called electrical electroconductivity because all salts in aqueous solution are electrically charged, and moving electrical charges generate a flow of current, this current or ionic conductivity is what these devices measure
A value above 2.2 micro S/cm is toxic to the roots. This value tells us that water has an excessive salt content for two reasons:
-Or the irrigation water you use is not osmosed and is very hard
-Or it’s osmosis but you’ve overdosed on the fertilizer.
For hydroponic or aeroponic crops, continuous meters are used, which gives us the value instantly, but we can also see their variations, by adding fertilizer to the tank and shortly after. That way we can see the consumption of our plants as they grow.
– pH of water grown in soil or hydroponic
– Recommended EC value of water in soil and hydroponics
⛳ Reverse Osmosis to treat your irrigation water
Marijuana is an “irrigated” plant, she loves water, but not just any water, in fact, she is a lady of high stature, even with a noble title, and as a queen she likes quality water. This is why we need to use water that can be pretreated with a reverse osmosis filter to remove lime, excess chloride and heavy metals
Some filtration equipment incorporate activated carbon absorbents, this element eliminates the organic matter in suspension, or dissolved, which is highly polluting, leaving you with pure water for the health of your plants, and of course yours, because if your plant is clean your green medicine will have a quality that you will notice in your final harvest.
If you don’t have an osmotizer, you can start by removing the chlorine from the water at home. One way is to obtain water from the tap in a bucket enough for two weekly waterings, and let it stand for 24 hours. The most efficient way is to obtain it from the mains as hot water, and when it is left to stand for 24 hours, it will remain at room temperature, eliminating chlorine with a good yield.
This osmosis water can be used both for your hydroponic system and for your traditional watering system with a shower and also for drip irrigation.
Here’s how to apply a watering timer.
➕ Continuous irrigation in hydroponic systems
Don’t go on vacation without talking to your plants. Its appearance will tell you how often they respond best to watering. A vacation is likely to last more than two days, so your plants will be very sad, and will tell you that they need some system to keep the substrate moist, without puddling it.
That’s why it’s ideal to have your own hydroponics system, with submersible pump, controlled by a timer; with this type of equipment you can go on holiday without worry, although it’s better to stay with your plants until they have finished their life cycle, it’s always better than being missed. Love is priceless.
✅ The watering frequency
The best time to water is half an hour after turning on the lights, as the plant changes its metabolism shortly after noticing the light, enters the light cycle, activates its metabolism again, and your plant enters a positive nutrient flow state again.
The nocturnal irrigations, favor the appearance of fungi, in addition we can harness the rot in the roots if we are using a substrate of flowerpot. The best thing is to have the roots in the air, in a well-assembled aeroflo system.
In flowering it should never be watered by foliar spraying. The buds are very easily contaminated with fungal spores, which very quickly find the ideal conditions to proliferate, if they are well established in a very wet bud. In addition, the relative humidity in the indoor air should not exceed 60% and if possible less, better.
If you are growing with conventional potted substrate, you may be more interested in installing a drip irrigation system. With a simple assembly, which incorporates an irrigation water and fertilizer tank, with a submersible pump controlled by a timer, irrigation pipes and pickets, you can perfectly forget about the irrigation, you just have to make sure that the tank has enough water to cover the submersible pump without it getting dry, because if this happens you will burn it.
You should also leave the proper pH and EC each time you add water or fertilizer to your irrigation tank. If the frequency you are programming is correct and drippy, you must adapt it so that the substrate does not get dry or waterlogged, always wet.
By means of the observation we will be able to know if they have excess or defect of watering, if the pH or the EC are not the correct ones, or if you have gone too far with the fertilizer or you have chosen a bad substrate.
✨ The shower, my best companion
Sometimes we prefer to do things the traditional way, and we are soil, pot and shower growers.
If that’s your case and you don’t have an indoor hydroponic or drip irrigation crop with a timer, we give you a series of recommendations for your best crops::
-Apply the jet of water with your shower to the base of the stem, and from a very low height, because if we make the jet fall down with force we run the risk of leaving a part of the roots exposed, facilitating rotting and direct access of the roots to any plague, if you are in summer, the temperature of your crop can skyrocket. Either you use air-conditioning systems or your plant is going to sweat like hell. In that case we recommend daily watering. Plant transpiration makes the plant consume much more water in order to stay cool, it is the same mechanism that humans have when they sweat…well, almost the same…so fill your shower with fresh water, measure pH and EC…and water!!
-In this environment the water of the substrate evaporates faster, to avoid this, we can make a compost in the pots adding a layer of balls of arlite (or expanded clay), to retain more moisture, as it acts as a protective layer in the substrate against evaporation.
You can carry out your subsequent watering by wetting the arlita with the watering can, which will expand the moisture throughout the substrate making your watering more efficient.
✌ Conclusion
We hope you found this whole series of tips helpful. You make the subject matter of our posts possible, since we rely on the doubts you transmit to us as well as the results you show us in your crops.
Before that, we can only say…thank you very much!
Keep up the good work!
Don’t forget to share our posts, and if you have any doubts or want to ask a question, don’t hesitate to do it, our technical department will try to answer you as best as possible.
See you at the following post?
See you soon!