In constant struggle for the regulation of cannabis, mainly in the medicinal field.
10-01-2018 12:21:54 - Updated: 10 January, 2018
Dear Cannalovers…
Thank you very much and welcome to John’s lab!
With this manuscript I hope to serve as a guide in order to show you everything you need to know to take your marijuana crop to the top, either as a recreational user or as a medicinal user.
I have worked on developing both this handbook and the advanced book for a few months, with the invaluable help of my colleagues at PEV Bank Seeds, so I would not like to continue without first thanking, Alan Martínez for his input and ideas based on the writing in the online blogs demarihuana.es and pevgrow.com, to Raquel Requena for his tireless transmission of concerns and advices from our customers, to Joserra Cabrejas for transmitting to me how the cannabic sector is developing on the Internet and of course to my colleague Amparo Fernández for raising our dratting process in Spanish to the French world.
? Introduction
First of all, before you start with your first marijuana crop, it’s important to have some basic knowledge. This free guide is just a simple introduction, so that you can then choose to become a true specialist or professional cannabis specialist, and do so with the best possible judgment, applying knowledge based on the latest scientific advances, either from the point of view of plant biology, agronomy, extraction chemistry and medical applications of cannabinoids and terpenes.
In other guides published on our website, you will have the opportunity to learn about the pests that affect marijuana, as well as a medical guide with the latest advances on cannabinoids, terpenes and other compounds extracted from cannabis, with possible applications in food such as superfood, cosmetics, herbal medicines and other active ingredients extracted from cannabis.
In this small guide I try to make you love the plant, not only for its economic value, but also for its ecological and spiritual value, learning to value its nature and what it can bring you to grow it, knowing what it feels like to be an integral part of a natural environment.
In that sense I will give you basic notions about what a marijuana plant is and what it needs to grow properly.
Although this guide is only an introduction to growing, we have prepared a small list of cannabis genetics so that you can choose the right marijuana seeds to grow, taking into account your individual preferences, or the medical treatment you need, whether you are a recreational or medicinal user.
Although, as you know, at PEV Bank Seeds we specialize in the preservation and production of cannabis seeds. If we refer to the net dry bud production you can get we talk about that in about 100 days you can get over 500 grams per square meter.
With your subscription, you will be able to keep up to date with the latest developments in growing, related equipment and the most important new marijuana genetics in the market.
And already you know! If you find a problem, or simply have something to tell us or share with us, please do not hesitate to do so, we will take into account all the opinions and our experts will be able to resolve any questions you may have.
I hope you have fun with us and have a happy growing.…? For a universal medicine…
⭐ General aspects of cannabis growing

Cannabis Sativa L. is an annual plant, this means that it germinates, grows, blooms, reproduces and dies in the same year. Naturally, which also occurs in industrial hemp, it germinates during spring, grows until about the middle of summer and from there begins to bud, producing seeds in turn in the bud for reproduction
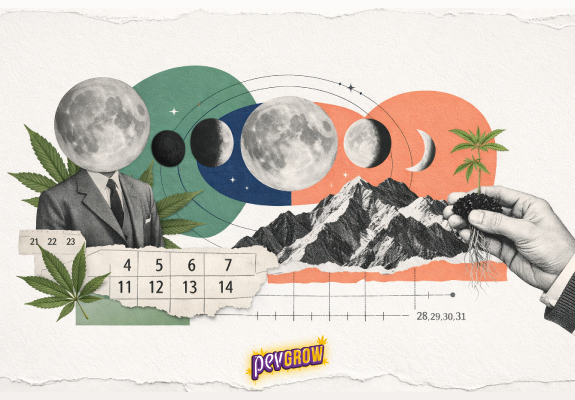
Cannabis is not a root plant, nor a leaf, neither is it a fruit plant, but a flower plant, so we can learn to work the biodynamics of the crop to improve our flower production, taking into account the lunar cycles and their influence, when sprouting, treating pests, preparing home fertilizer, pruning, how to make cuttings, harvesting and curing.
In the natural environment, when the seeds are already mature, the plant dies, the seeds fall and begin to germinate in the following spring, remaining in latency period during the winter, since in order to germinate correctly the conditions are high humidity and temperatures above 18ºC.
Why is it important for you to know this?
Because it’s crucial to know how to germinate properly the seeds that you purchase, as well as you must also know why a plant can stop growing and / or delay its flowering.
In this basic guide I will give you the notions so that you can begin to know the complete cycle of a plant and its conditions so that it develops correctly.
The vegetative cycle of the cannabis plant
The seeds of the cannabis plant do not become active if they have not been dormant at low temperatures for a few months. This is why the seed banks store the seeds in special vacuum containers, with moisture absorbers at a temperature of 5ºC for at least two months.
Once the temperature rises and the seeds absorb enough moisture, they are ready to germinate.
The seed production process is also very important, since if they take too much moisture during the autumn (or during their production when they are forming in the bud), it is very likely that they will not germinate, or the seed may open well but the radicle will eventually stop growing.

If the temperature is ideal for germination but the humidity is scarce, the seed will continue to be in latency period, being this a very effective mechanism of preservation of the species, so that with this, nature tells us that the seed will only germinate in case the conditions are ideal, so that the species only may subsist in the best conditions… …awesome!… right??
This is how nature teaches us to recognize the arrival of winter, when the days begin to get shorter after the summer solstice; in the middle of summer the plant begins to “become aware” that it receives fewer hours of light. That is the sign that nature gives it to begin its flowering and thus its process of reproduction.
From that moment on, the plant begins to develop buds that will later be ready to receive the males’ pollen, be fertilized and produce seeds.
In the case of the cannabis plant that produces THC (marijuana) we can say that it grows very poorly in winter, so that outdoor crops are adapted to give a harvest per year, but as we in our indoor crops can reproduce the conditions in which the cannabis plant develops faster and gives more yield….
… you will be able to carry out between 4 and 6 harvests a year !! Isn’t that great??
⛳ How do we distinguish a male from a female?
The Cannabis Sativa L. as THC Chemotype producer, is dioic, that is, for its reproduction there are plants that only generate male flowers (staminiferous) and plants that only generate female flowers (pistiliferous). The male plant pollinates the females, which do all the work to develop the new offspring… Basically the same as humans!
As a seed bank, we are very interested in males for the stabilization and production of seeds, since they are the ones who contribute dominant genes for the production of cannabinoids and terpenes..
Female plants are of interest to us as a final product (the buds) and are used to investigate, smoke, extract their resin in the form of Hash, or to perform somewhat more sophisticated extractions processes (medicines and food).

In short, we are interested in female plants as a product only NOT pollinated (i. e.,”sinsemilla”) to be able to take advantage of the potential that the plant has in its biosynthesis of cannabinoids and terpenes. Males also have THC, CBD and terpenes, but in much lower concentrations.
It is the female plants that contain large amounts of THC (Marijuana) and/or CBD (Hemp) and are responsible for producing buds loaded with resin glands, glands that are enhanced if the crop has been grown without pollination, as mentioned above, “sinsemilla”.…which is precisely what you want to get, right??
It’s very common (relatively) for us to find a hermaphroditic (monoic) marijuana plant, this means that it generates both male and female flowers, so it can fertilize itself. This is almost always the case with hemp for fibre and CBD production, because it’s in general monoic, and it also may occur with dioic marijuana plants that have suffered some type of stress during growing, such as hydric stress (lack of irrigation or excess of fertilizer), luminous stress (sudden changes of photoperiod in an indoor crop), or environmental stress as sudden increase or decrease in temperature or humidity, for example in the environment.
If you can control the right conditions for the development of your plants you have almost everything well done!
✨ Chemotypes in cannabis: Marijuana (THC) and Hemp (CBD).
Cannabis is a plant of absolute natural wealth, which has been used for centuries due to its medicinal properties and its pharmacological effects on the central nervous system. Besides, It’s like the pig industry, everyone may take advantage every part of it!?
The plant gives us fiber for textiles, food, medicines, biofuels, building materials, is a strong regenerator for the soil, air purifier…
As a pharmacological reference, cannabis is represented by two main active ingredients which are THC (Tétrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol).
That means we can find two clearly differentiated chemical genotypes (chemotypes), i. e., two clearly differentiated genotypes in the chemical composition of their harvested flower, general chemotypes producing THC (Marijuana), and general chemotypes producing CBD (Hemp). Although there are several subtypes that refer to different cannabinoid ratios, for the moment, we leave it in this simple idea to make it simplier and clearer.
The two chemotypes are Cannabis Sativa L. and within each of them there are more differentiable chemotypes as I have just mentioned, but these are only capable of expressing their adequate composition by changing the environmental conditions, this is what is known as phenotypic expression, or phenotype.

In general, the environment is as important as plant genes.
The THC producing cultivars are psychoactive genetics, which means that their chemical composition gives rise to an active substance in the brain, but also alters the states of consciousness, in fact, from the legal and pharmacological point of view, THC is a psychotrope. Not to mention the other substances that alter THC activity. But, take it easy!
What I want now is make you understand the value of the seeds and its growing environment, since it’s you who are going to control them!
I would also like you to learn how to select your seeds by sorting them by effects and flavors. I say this because there are people who need their medicine to have the desired effect, minimizing unwanted effects….. and you know… each person has a different way to react to every medicine. I also need you to understand that the same genetics, grown in the same way, and with “the same composition” doesn’t have to produce the same effect on people.
THC has activity because it is the “key” (or one of the many keys) that fit into biological “locks” called cannabinoid receptors, (CB1 and CB2 receptors) found in animal cells.
The mechanism is very simple, so that the THC “travels” through the bloodstream, and when it reaches a receptor located on the surface of a cell (lock), it is introduced into this and “opens” it, triggering a series of biological responses, one of them: the appetite for sweet food.

THC generally tries to imitate one of the most beautiful and sympathetic molecules that animals produce naturally: La Anandamide (although there are more endocannabinoids in the body).
Anandamide is a Sanskrit term (language originating from India), which means “happiness”. It all begins with the origin of marijuana, and its pharmacological uses already used in India since ancient times. That’s why the English rediscovered it in Victorian times, calling it Indian hemp.
Anandamide is very important both in the brain and in other tissues, and is part of the so-called Endocannabinoid System (ES), which is, the Cannabinoid system widely extended in the animal kingdom, ie, your body is continuously synthesizing cannabinoids without you may be aware of it….
…amazing, isn’t it??
In short, both anandamide and other endocannabinoids (of which I speak in the medical guide) are involved in such important processes as short term memory and memory formation, learning processes and motor skills control.
This could be one of the reasons why you have bright ideas when you’re smoking!
CBD or cannabidiol is a molecule also active in the brain, but it is NOT psychoactive, since it does not alter the states of consciousness and therefore, it is not considered psychotropic.
The marijuana plant also contains CBD, although it rarely exceeds 1%, the opposite of what we may find in hemp plant.
CBD acts pharmacologically through mechanisms other than THC, in fact it does not act through the same receptors as THC, so it influences the effects of THC, cushioning the psychoactive effect and enhancing its medicinal effects in the brain. This pharmacological mechanism of positive synergistic activity or concomitant medicinal activity is called the «entourage effect» and is useful for cannabinoids but increasingly takes into account the effect of terpenes.
In summary, marijuana strains with high concentrations of CBD, or special cultivars created to develop special THC:CBD ratios are the most suitable for medicinal users. The higher the concentration of CBD in proportion to the THC content, the lower the psychoactive effect, and the greater its potential as potential medicine.
Other very interesting cannabinoids to consider in cannabis strains, most of them now under research are: CBN, CBC, CBV, THCV, CBDV, CBCV, CBG, CBGN….although there are many more derivatives of these. all these are considered now as “compound families.
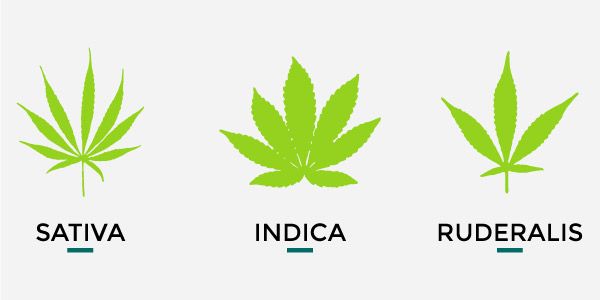
? Different genotypes of marijuana: Indica, Sativa, Rudelaris, and hybrids.
The genotypes of marijuana can be classified into three groups according to their physiognomy and agronomic value: Cannabis Sativa Indica, Cannabis Sativa Sativa and Cannabis Sativa Rudelaris.
Cannabis Sativa Indica
Original from India, Pakistan and Afghanistan, it is a medium-sized plant with large leaves of broad petioles and a dark green color.
It has short flowering periods from 55 to 75 days. These plants have relaxing effects due to the higher CBD content and characteristic terpenes.
Cannabis Sativa Sativa
Although a common Asian origin has been demonstrated, it is genetically adapted to tropical climates with higher ultraviolet radiation index and longer photoperiods. That is why its leaves are smaller with narrower petioles and a lower level of chlorophyll (a less intense green) than the indica genetic.
They are plants that become very high, with very long flowering times (up to 100 days), and with very high THC content, are few producers (referred to dry bud weight) but the most psychoactive. They have energetic effects, hardly any CBD and their flavour is citric and lemon-flavoured (in general, more monoterpenes concentration).
Cannabis Sativa Rudelaris
Very common steppe strain from Central Asia. Small plants with little interest for the production of fiber or resin, but with a very important trait: Its flowering is not induced with the change of photoperiod. This is due to its evolution in cold climates and its adaptation to photoperiods with a low number of hours of sunlight, and with almost insignificant sun radiation indexes.
Most of the marijuana seeds you will find on the market are hybrids between the first two subtypes, or between the three if we are talking about an autoflowering strain. Over the past 30 years, seed banks have been able to stabilize hybrid strains by selecting and crossing plants with special genetic traits over time (e. g. hard and heavy buds of an indica strain combined with a higher THC level of a sativa genetic).
The same can be done to modify the aromas, flavours, hybrid vigour etc…
It is recommended for beginners to start with simple and highly pest-resistant cultivars with very high yields, such as genetics of Skunk generation, some “white” strain (White Widow) or an hybridized Haze.
☕ Marijuana Seeds: Regular, Feminized, and Autoflowering.
A plant is always developed from seed (sometimes from cuttings, but at some point it was started up from seed).
To determine what kind of marijuana genetics you want to grow, the first thing you need to know are the possible types of seeds to introduce into your crop
You have three possibilities:
Regular Marijuana Seeds
With the purchase of regular seeds, you are buying both male and female plants statistically at 50%.
So you’ll have to make sure you remove the males ( already sexed) when they start to show the sex (it shows the pre-flower). If you do not, the males will develop pollen that will be spread in the growing space, the females will be pollinated and therefore your buds will be full of seeds (which, by the way, will also be regular seeds).
There are experts who say that a regular seed keeps its true genetic essence of marijuana, and therefore its original flavor and effects. I believe that the originality of a genetic is lost when it is crossbred with another strain that is not the same one, whether it is stable or not, regardless of the pollen reversion process, since this only affects the chromosomes that define sex. We will discusse this in the advanced guide.
Feminized Marijuana Seeds
These seeds will only give you female plants in a 99% of probability this means that this type of seeds will be exclusively female plants. Although they have also been shown to be more susceptible to hermaphroditism triggered by certain types of stress.
As a seed bank, PEV Bank Seeds specializes in the development and production of feminized seeds, stabilizing genetics through the use of STS method.
We can see that we do not notice differences between a regular strain and the same genetic reproduced in feminized format. However, we cannot say the same for Autoflowering plants.
Autoflowering Marijuana Seeds
This sort of seeds introduce the most important Rudelaris trait, i. e. that they are cultivars that do not depend on the photoperiod. rtant Rudelaris trait, i. e. that they are cultivars that do not depend on the photoperiod. This agronomic improvement saves time for the cannabiculturist, since it shortens the growing period (the plant starts to bloom “when they feel like”). This, in an indoor crop, sometimes means to obtain small plants, something bad from the yield point of view, and something good, if we look for a discreet crop; in outdoors, it means to have a greater number of harvests per year.
? Outdoor and indoor crops.
As we have mentioned before, the marijuana plant executes its vegetative growth period until it notices the change of photoperiod and the number of hours of sunlight begins to decrease.
So we will have the plants ready to harvest, as early as mid-September. We will know that it is ready when approximately half of the pistils have turned brown.
Another way of checking it out is through a microscopic with one thousand of magnifications, watching a large part of the trichomes turned opalescent.
In indoor crops we have to install low power LED lamps (or the new LEC technology) or the typical high intensity HPS lamps, so we can manipulate the amount of light provided (intensity), its spectrum (if it is blue light for growth, red for flowering, or mixed, for both vegetative phases).
That’s the way to tell the plant to start blooming, reducing the hours of light (to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness), et en lui communiquant l’arrivée de l’automne (spectre rouge de la lampe).
It’s very simple. During the growth phase for feminized seeds, you should keep a fixed photoperiod of 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness, during four weeks; once these four weeks have passed, we change to a photoperiod of 12/12 h until the end of flowering.
Growing a marijuana hybrid from high quality seeds can take three months. So we advise you, in case you have a room with enough space, to start with a “growth room”, this room is only for seedlings and growing plants, in order to harvest continuously, reaching up to 6 crops per year. While flowering is underway in other room, you can begin to germinate the next harvest.
We use those “growth rooms” for keeping mother plants!… interesting, right??
? Growing marijuana as “seedless” way
There are three fundamental ways to grow “sinsemilla” female plants:
- Starting up from regular seeds: Removing the male plants during sexing.
- Buying or preparing the cuttings yourself: The main advantage of clones is that you save germination, and they are also an exact copy of the original plant. The disadvantage is that if the plant is not of quality the cuttings either, and besides many are not reliable, because if they have some plague you end up taking it too.
It might be a good idea to get your own cuttings from a plant selected by you, it is something you will see exposed in our advanced cannabis guide. - Starting up from feminized seeds: This is highly recommended, provided it comes from a reliable seed bank. Look for seed banks that publish the certificates of analysis of their cultivars by a laboratory specialized in cannabinoids and terpenes.In that sense our friends Iñaki and Ángel from Fundación Canna are excellent professionals, and they analyze the samples of Cannabis with the maximum accuracy and precision, many seed banks work with them.

✅ Conclusion
Now that you know the basics, it’s time for you to start applying it and get your marijuana seeds as well as all the material to get started.
Our technical department is available for you at any time you need it… and remember… if you want to go deeper do not hesitate to adquire our Advanced Cannabis Guide at an excellent price.
We also hope you enjoy the discounts and promotions of our online shop pevgrow.com
Peace and Love??
John G. “White” , Pevgrow technical team.