What is happening to my system? This is one of the questions we are asked most often in our growshop, and it is that during the cultivation of cannabis in addition to a good choice of marijuana seed, certain problems can occur that must be prevented or corrected so that they cause as little harm as possible. At Pevgrow we want our customers and friends to get always the best results, and for this reason we have decided to create this article in which we will look at the problems that usually arise and the best way to solve them.
⭐ Deficiencies, excesses and blockages of macro elements
The macro elements are 3, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and are those that plants need in large quantities throughout their life. They are elements mobile, which means that when they are missing to form new shoots, the plants take these nutrients from the reserves of the older leaves, so it is these that show the problem.
When marijuana is deficient in any of these nutrients, it is said to be lacking them, and it demonstrates it in a certain way that needs to be known so that the problem does not escalate. If the deficiencies of these elements are not corrected, the plant will not be able to fully develop and its production can drastically decrease, so we must know how to recognize them as soon as possible and act accordingly, so we will go to see each of them in detail. individual.
Nitrogen Deficiency
If the lower leaves of the plant begin to lose their deep green color, it is very likely that there is a nitrogen deficiency. This problem is more likely to occur during vegetative growth and pre-flowering than during flowering or bud ripening. The wear of the blade is uniform normally, from the outside to the inside, although sometimes stains can appear, as if it were withered, to the point that if it is not corrected it ends up coming off.


11-02-2022 09:00:29 - Updated: 11 February, 2022
Why is there a nitrogen deficiency?
It can be for various reasons, because it has less availability of this nutrient than necessary, because the PH is inadequate and cannot assimilate it, or because there is an excess of salts or other elements that cause nitrogen blockage. It could also be due to a secondary factor, such as a problem in the root system or a mismatch in environmental parameters.
If you grow in soil, there will come a time when the plant will consume all the nitrogen reserves of the substrate, and from then on you will have to transplant or give the food mixed with the irrigation water. It is important that the irrigation nutrient solution has a pH of around 6.0 so that the nitrogen is assimilated as soon as possible.
Excess nitrogen
Excess nitrogen occurs when we give the plant more of this element than it can absorb, and it causes a toxicity that plants show with a darker color of the leaves and by folding claws the tips of the leaves into. In some cases, burns can also be generated on the tips of the leaves, which become very hard and with different shades of color.
An excess of nitrogen can be even worse than a lack, because plants stop their development and can even die if not corrected. If this problem occurs, the best thing you can do is wash the roots so that some of the nitrogen is leached and remains in the necessary amounts.

Blocking of nitrogen
Among the nutrients that plants need there are compatibilities that can create a positive synergy, just as there are incompatibilities that can cause problems, they are the antagonistic elements, and you have to watch out for them.
An excess of potassium in the soil can lead to poor assimilation or direct nitrogen blockage, and if we don’t act quickly, the problem will increase. If you use fresh water, regulating the PH, and take into account the amount of food that contains the substrate, it is difficult to suffer from nitrogen blockage, but if one of these variants fails and you do not recognize the problem, the most normal thing is that you think that the plant lacks nitrogen and increases the dose, creating a greater problem in some cases.
Deficiency of phosphorus
Another shortcoming that occurs in the lower leaves and older plants, because it is a moving part. In this case, instead of turning pale or yellow, the leaves can take on a bluish tinge and stains or signs of wear on their surface. Another symptom that often occurs with phosphorus deficiency is that the petioles that join the leaves to the trunk become dark, purple, or red.
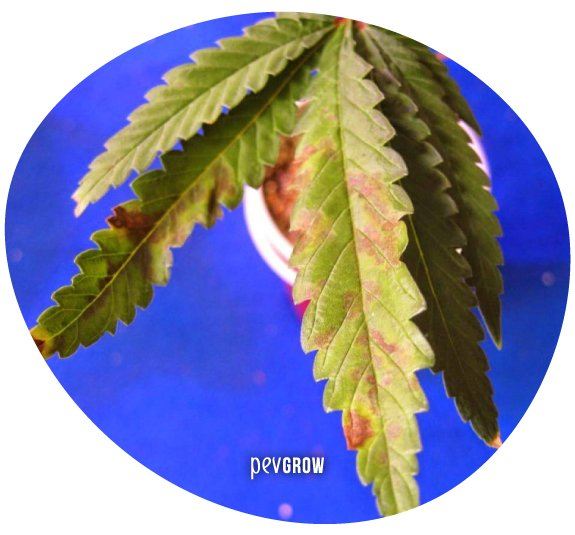

Why does a phosphorus deficiency appear?
The lack of this element in marijuana crops usually occurs during the flowering phase, i.e. when the plant needs it in greater quantities. As with nitrogen, phosphorus deficiency can occur due to its lack of availability, an incorrect pH of the nutrient solution or substrate, or an excess of salts caused by irrigation with very hard water or too much fertilizer.
Excess of phosphorus
The consequences of an excess of phosphorus can be very serious because, among other things, it decreases the absorption of other nutrients such as iron or zinc, among others. One of the most visible symptoms is that the leaves become very dark and begin to appear spots, mottling or mosaic patterns, which are signs of the nutrient blockage it causes.
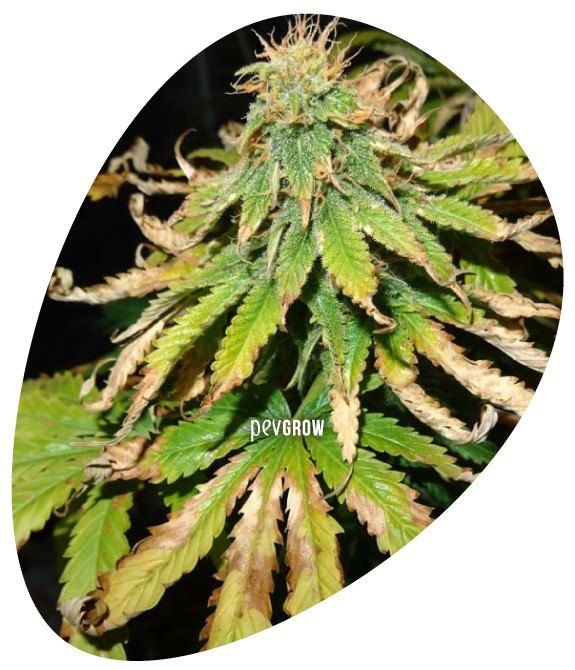

Phosphorus block
Deficiency caused by blocking other nutrients does not usually appear in cannabis crops, but sometimes the blockage occurs for other reasons. Very compact soils, poorly ventilated, and with a low content of organic matter can cause problems with the assimilation of phosphorus. Low ambient temperature, relative humidity or too low or high can also affect the absorption of this element, to pests or as root problems.
Potassium Deficiency
Potassium is the second most important element among all those involved in the cannabis diet, and for this reason its lack, excess or blockage can lead to a large loss of total production. When a plant is deficient in potassium, it can be clearly seen in its lower leaves, which begin to yellow from the edges inward, keeping the midsoles green where the nerves are.
This problem can occur at any stage of the crop, but has worse consequences when it occurs during the flowering phase, as one of the functions of potassium is to compact the buds, so in addition to seeing the affected leaves you can check how the rate slows down. fattening of flowers.

Why does a potassium deficiency appear?
It can arise for various reasons, due to its lack of availability, due to an inadequate PH, too hard irrigation water, or due to an excess of nitrogen. When it appears in growth it may be due to an incorrect PH or an excess of N, but in flowering it is more common than due to a lack of sufficient availability.
Excess of potassium
The biggest problem caused by excess of potassium is the blocking of some nitrogen, magnesium and some trace elements, and it is also difficult to identify because it is often confused with other deficiencies. Fortunately, it’s not one of the most common cannabis problems, and if you suffer from it, it can be easily fixed with a root wash.
Potassium Blocker
Ammonium (nitrogen) and potassium cations are monovalent, so there is an antagonistic effect between their ionic forms. What does this mean? Well, the more there is, the worse the assimilation of the other will be. This can be a problem during cultivation, as we can confuse blockage with a deficiency and add more fertilizer, further accentuating the problem.
⛳ Calcium, magnesium and sulfur, the secondary elements
After the macro elements, the secondary elements are those which plants need in the greatest quantity during the whole crop. Of the 3, calcium and magnesium are the most important, decisive for the perfect development of plants and must always maintain a balance between the two.
Calcium deficiency, excess and blockage
In outdoor crops in mother soil, it is not very common, because calcium is usually present in large quantities in the soil. But in hydroponics, aeroponics or even coconut fiber it is quite common, in addition to crops on land where it is irrigated with fresh water or osmosis.
Calcium deficiency manifests itself in the upper shoots, since it is an immobile element and the plant cannot carry it. You can see how the new leaves come out deformed, smaller than usual, and with a lighter or yellowish color. This deficiency can be corrected by adding calcium as a mono-element, by mixing tap water with osmosis water in subsequent irrigations, or by adding a calcium / magnesium solution such as Calmag by Biobizz, Canna or Atami. The best thing is that you use one of these commercial products that have an equal distribution between calcium and magnesium, remember that both elements must always be kept in balance. Excess calcium manifests as a lack of other nutrients such as magnesium, potassium, iron and manganese, although the most noticeable are usually the top 2.
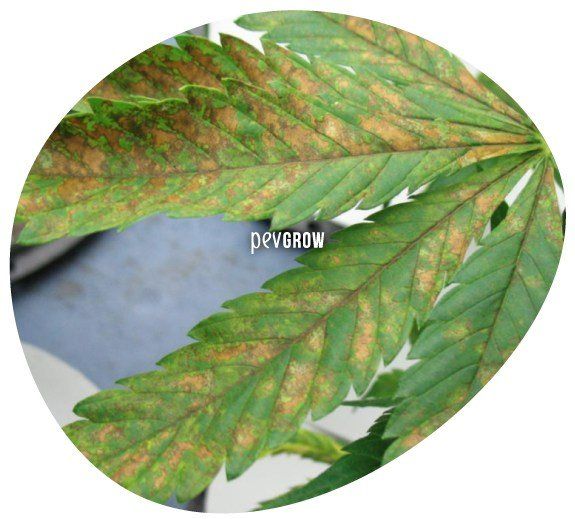

Deficiency, excess and blockage Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency is one of the most typical in cannabis crops and this intermediate element is required in large quantities and there are several factors that can prevent it from being properly absorbed. One of the reasons why a magnesium deficiency is created is due to an inadequate PH, but on many occasions the problem comes from excessive humidity or low temperature of the substrate.
Magnesium is a mobile element in the plant, so it can be transported from leaf reserves to new shoots. The lack of this element manifests itself in the older leaves, usually in the central and lower part of the plant, which begin to yellow between the nerves and in some cases the edges are folded.
An excess of magnesium causes toxicity that can greatly reduce overall production if not treated in time, but it also leads to blockages of other nutrients such as calcium. Fortunately, it usually doesn’t show up very often, and the solution is also easy, as the magnesium is easily dragged along by leaching, so with a light washing of the roots it resolves.
Magnesium blockade usually appears normally due to excess calcium, especially in crops where they are irrigated with tap water. To a lesser extent it can be caused by excess potassium or hydrogen caused also, but using cannabis-specific substrate and fertilizers it is difficult to cause blockage.

Sulfur deficiency, excess and blockade
Within the intermediate or secondary elements essential for the development of marijuana plants, sulfur is what they need least, but it is important to know their behavior in order not to have nutritional problems or imbalances. Sulfur is a semi-mobile element, which means that it has a certain mobility in plants but depends on several factors.
When sulfur deficiency appears due to excess nitrogen, it is noted in the most recent leaves, which are born with lighter or yellowish tones, very similar to iron deficiency. When sulfur deficiency occurs due to a general nutrient deficiency, it usually occurs in older leaves, although this is less common. In both cases, one of the most likely symptoms is a slowdown in the rate of development.
An excess of sulfur causes an abnormal development of the plants, which form smaller leaves, somewhat deformed, with more vivid and darker colors in the central parts, and with yellowish margins. Normally this excess usually has no serious consequences, as long as the EC is not too high.
Sulfur blockade usually appears due to an incorrect pH or an excess of calcium, but in this case it is because both have precipitated and a residual gypsum is formed, which prevents the absorption of both elements. This problem is more common in hydroponics and is one of the reasons why some fertilizers are usually offered separately in 2 parts, A + B.

✨ Deficiencies, excesses and blockages of microelements in crops of marijuana
The microelements or micronutrients are those nutrients that the plant needs less than the macroelements. This does not mean that they are not important, as they have basic functions for perfect development in all stages of the crop. Fortunately, by using soil and specialty commercial cannabis products and adjusting the PH of irrigation, micronutrient deficiency, excess or blockage problems are unlikely to occur, so we always recommend investing in reputable brands.
Iron deficiency, excess and blockage
Iron is an immobile element in plants and is also difficult to absorb because it requires a PH below 6.5, so it is easy for iron assimilation problems to occur in cannabis crops. This nutrient is very important because it is involved in electron transport and sugar management, as well as having vital functions in photosynthesis and other processes.
When plants suffer from iron deficiency, they manifest it with a progressive yellowing of the younger leaves, from the center to the edges. Fortunately, this problem can be easily corrected by spraying chelated iron if it occurs during the growth phase, or by watering with an iron-rich mono-element fertilizer if it occurs during flowering. Check the PH to make sure it is below 6.5 which is the best way for plants to absorb iron. Excess iron is rare in marijuana crops and appears with a brown or coppery color in the leaves. If you think your plants have an excess of iron, you can easily fix this with a root wash.

Zinc deficiency, excess and blockage
Zinc is essential for the formation of growth hormones such as auxins and helps create chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. When a plant suffers from zinc deficiency, its development slows down and chlorosis manifests itself in younger leaves in the form of burns at the edges of the leaves. It can also cause misshapen or abnormal growth of new leaves, and in some cases the distance between the nodes is drastically reduced.
Zinc deficiency is usually caused by an excess of other nutrients, so the most interesting way to fix this is with a good root scrub. Another way to overcome this deficiency is to apply a single element fertilizer rich in zinc, sprayed during the growth phase, or irrigated if you are already in the flowering cycle. Excess zinc is very rare in cannabis crops, but when it occurs it can be a serious problem that can lead to plant death. If you suspect that they may have an excess of this trace element, I recommend that you do an urgent radical wash, adding enzymes to the water to help dissolve the accumulated salts.
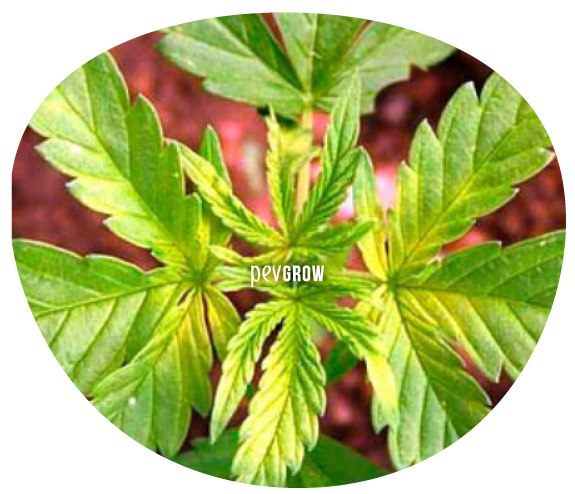


Manganese deficiency, excess and blockage
Manganese participates in various enzymatic and photosynthetic processes vital to marijuana plants and also acts as a defense against situations of water stress, excess salts or lack of oxygen. However, it is consumed in small quantities and should not normally be missing in normal crops, although it is important to know the symptoms so that the problems do not get worse.
The first signs of a manganese deficiency can be seen as a decrease in the speed of growth or flowering, which can stop completely if not treated in time. Can also be observed abnormal development of the younger leaves, gradually spreading to the rest of the plant’s leaves. An excess of manganese causes oxidation on the leaves which can be seen as orange spots that take on a brownish hue as the problem progresses, and normally causes iron and zinc block deficiency, but this is easily remedied with a root wash.

Deficiency, excess and blockage of boron
Boron is a vital microelement for plants because, together with calcium, it is responsible for the production and strengthening of cell walls, as well as acting in management of sugars and carbohydrates among other things. Other functions of boron are nitrogen metabolism, it is involved in the production of certain proteins and hormones and helps in the formation of inflorescences that will eventually become large buds.
Boron deficiency is rare in cannabis crops and usually appears when there is a lack of irrigation or too low ambient humidity, although it can also be caused by a blockage caused by excess salts accumulated in the substrate. The first thing you notice is a slowing of the growth rate of the plants, but the most visible is an abnormal growth of the shoots, which appear with light green spots or burns in some areas. Excess boron is also not very common in marijuana crops, and the signs are similar to other nutritional toxicities, such as burnt leaf tips or edges. If not treated in time, the necrosis advances to the center of the leaf, drying completely and causing it to fall off, but you must know that this problem is easily solved with a good root washing.

Molybdenum deficiency, excess and blocking
Molybdenum is the least used micronutrient by plants, but that doesn’t mean it’s irrelevant, as it is necessary to transform phosphorus and nitrogen into elements assimilable, in addition to participating in the synthesis of amino acids. It is one of the few mobile microelements present in plants, and normally in normal crops molybdenum is not usually deficient, but it is important to know the symptoms of its deficiency so that the problem does not cause production losses.
Being a mobile nutrient, molybdenum deficiency manifests itself in older leaves and those in the central part of the plant, and care must be taken as it is easy to confuse it with a magnesium or nitrogen deficiency. If you see the old leaves in the central part of the plant starting to yellow around the edges, they probably suffer from molybdenum deficiency, especially if you see appearing pink or orange spots. An excess of molybdenum causes iron deficiency blocking, and is evidenced by a strong yellowing of the leaves of the new shoots. Molybdenum block is very rare in cannabis crops, as it is needed in very low proportions.

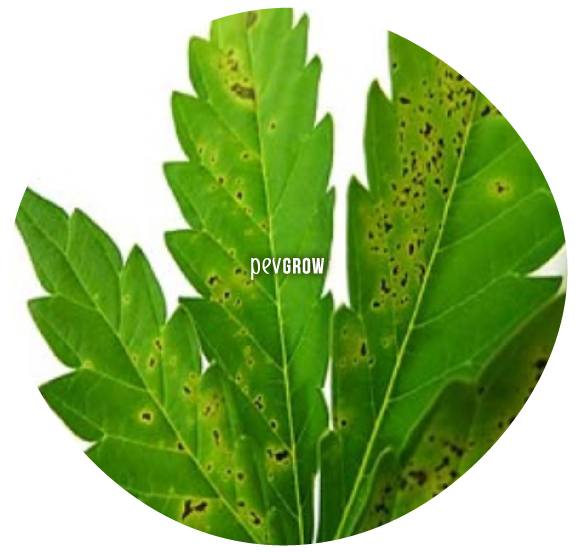
Lack, excess and blockage of copper
As with molybdenum, copper is a micronutrient that is hardly required in cannabis crops, but it fulfills some important special missions. This element is essential for carrying out numerous photosynthetic processes, promotes enzymatic activity and enhances the aroma, flavor and color of the buds. Another important function of copper is the protection of the root system from attack by fungi, which is why it is used both as a fungicide in indoor and outdoor crops.
Copper is immobile in plants, so its deficiency manifests itself in the leaves of new shoots, which are born of a lighter color, with some deformations, and black spots may appear in some areas. This deficiency is similar to that of calcium, so care must be taken not to confuse it. If this happens to you, you can spray the leaves with a copper-rich fungicide, always with the lights off in indoor crops, or at sunset in outdoor crops. Excess copper does not usually occur with marijuana, but if you suspect your plants may be suffering from it, it is best to irrigate with plenty of water to correct it.

Deficiency, excess and blockage of chlorine
Chlorine performs several important functions in cannabis plants, as it activates enzymes such as amylase or asparagine synthetase, among others. Together with potassium, chlorine acts on the opening and closing of the stomata, thus intervening in the regulation of transpiration and internal humidity. Chlorine is highly mobile in some crops and is rapidly transported to areas with physiological activity, but in the case of cannabis this is usually not the case, so it behaves like an immobile element.
For this reason, the lack of chlorine is found in new or younger leaves, where burnt tips or edges appear, which acquire tanned or pale tones. If at the time of transplanting you see that the roots have very thick tips, it is possible that they have a chlorine deficiency, especially if after transplanting the plant grows very slowly. The excesses of chlorine usually occur in crops where they are irrigated with very hard tap water, and the signs have to do with the accumulation of salts it causes, since it supposes the blocking of the absorption of many other nutrients. To easily solve this problem, you can wash the roots with distilled or osmosis water.
👾 Summary of excesses and deficiencies in the cultivation of marijuana

🎯 Things to be known to avoid these symptoms

✅ Conclusion
In this article we have intended to give you some tips to identify what your plant may be suffering but above all to try to prevent any future problems in your indoor or outdoor crop.
If your plant begins to show yellow leaves, we are sure that it is a minor problem that you can solve easily, also following the tips proposed by Pevgrow in this and other posts.
We hope you enjoyed it and do not hesitate to share your experiences with us, we will be happy to listen to you and learn new knowledge related to our sweet medicine.
See you at the following post?
See you soon






We I’ve had problems with what appears to be rushed I’m not sure quite what it is I think it is whatwe have it all over the trees around here and we got real hot the other day and it to have brought it on with the heat what could that be