Cannabis genetics are classified into 3 subspecies: indica, sativa and ruderalis. Among them they have many common features, but there are also a number of differences that it is important to know. In this post we will see the main qualities that distinguish the different varieties of cannabis.
📲 How are sativa cannabis varieties?
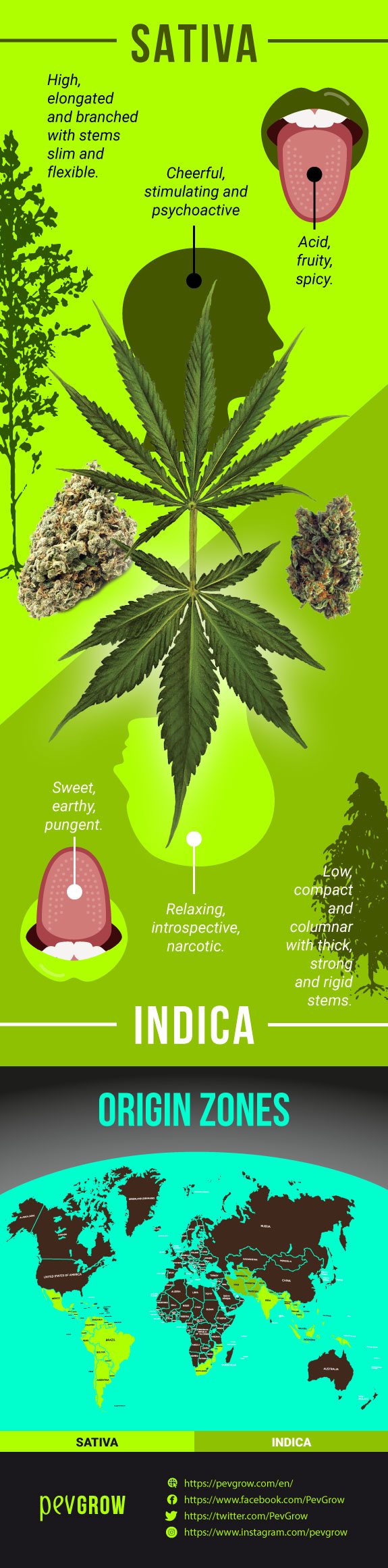
Sativa strains usually grow a lot, their morphology is elongated, with quite a lot of branching, wide distance between knots, and almost always thin light-colored leaves. Their life cycle is also quite long, it seems as if they are cooked on a slow fire, needing in many cases more than 8 months between the vegetative cycle and flowering.
In its chemotype is usually found a high content of THC and low of the rest of cannabinoides, and its terpenes profile is more varied than the rest of subspecies. It is believed that these changes are related to the type of light spectrum they receive, environmental conditions and probably other external factors.
🚀 Main differences between sativa and indica varieties
| Sativa | Indica | |
| Structure | High, elongated and branched | Low, compact and columnar |
| Trunk and stems | Slim and flexible | Thick, strong and rigid |
| Leaf | Thin, light and narrow leaflets | Thick, dark and broad leaflets |
| Flower | Elongated and aerated | Compact and dense |
| Root | Deep and slightly branched | Superficial and very branched |
| Flavor / Taste | Acid, fruity, spicy, etc. | Sweet, earthy, pungent |
| Effect | Cheerful, stimulating and psychoactive | Relaxing, introspective, narcotic |
| Resin | Fitted capitated type | Sessile capitated type |
| Chemotype | High THC | Medium THC along with other cannabinoids |
✅ Indica Vs Sativa
The most substantial differences between indica and sativa cannabis varieties are related to the environmental adaptation they had to undergo over the centuries. Indica varieties are concentrated in a smaller geographical area than Sativa strains that are present in virtually every part of the world.
Indica genetics spread to a relatively small extent, with most of them remaining in and around Himalayan mountains. Like Sativa varieties, Indica strains continued their journey from Central Asia to the Middle East, and then moved through North Africa, but no further than Morocco, and in Europe what we now know as Turkey.
It is possible that until that moment the classification between sativa and indica varieties had not been made, plants from Morocco, Egypt or Lebanon were rather hybrids, as well as those from northern India. However, those that continued through Pakistan, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan and all this area evolved until they achieved the qualities that we now classify as indica.
🔥 Characteristics of Indica strains
These were polishing their features due to the climatic and environmental conditions they had in their new environment. In high mountain areas, the short summer caused the flowering to be shortened gradually until in many cases it was in a much faster cycle than sativa strains. This is the reason why Indica varieties develop less and are smaller in size.
The lower luminic incidence made Indica plants create a larger surface of leaves, which in addition the not very fertile soil forced them to be thicker in order to accumulate more nutrients. The constant strong winds of the high mountain areas also caused the stems to become more and more strong, as well as the more compact and dense structure.
🎯 Characteristics of Sativa strains
However, sativa plants from the equatorial regions have completely different climatic and environmental conditions. The constant photoperiod, the heat, the very high humidity, the fertile soil and other factors forced these genetics to adapt differently.
The good climate for cultivation that they have in most equatorial, tropical and subtropical areas allowed sativa varieties to extend their cycle several months longer than those of indica plants. The high incidence of sunlight and permanent high humidity caused the leaflets of the leaves to become thinner and the structure of the plant to lengthen.
The chemotype was also mutated, probably by spectrum and light intensity, although this can be understood in different ways. Terpenes profile, like other plants in the plant kingdom, have been acquired according to the needs of their environment.
Infographics

03-01-2020 09:00:08 - Updated: 3 January, 2020
👾 Which are the best sativa varieties in the world?
It is difficult to say which is better, just as it would be impossible to say which fruit is the best in the world, because it depends on the context. First we would have to distinguish between commercial sativa plants and Landraces or pure sativa varieties.
If we take a look at the most consumed strains we can classify them in an objective way, but the best thing would be to analyse each of them separately to find out in which feature they can be outstanding, in order to be able to say that the one with the highest percentage of terpenes is the tastiest, or the one with the highest THC content can be the most psychoactive.
🎬 Best Landraces sativa plants
Based on the pure genetics most used to consume and to create new hybrids, we think that the best Landraces sativa varieties in the world are these ones:
- Colombian Gold
- Highland Oaxaca Gold
- Chocolate Thai
- Durban
- India Kerala
- Pink Sleeve
- Jamaican Lamsbread
- Maui Wowie
- Zamal
- Vietnam Black
🧐 Best commercial sativa plants
- Original Haze
- Sour Diesel
- Amnesia
- Destroyer
- Neville Haze
- Ed Rosenthal Super Bud
- Hawaii Snow
- Kali Mist
- Zamaldelica
- White Rhino
– Feminized Vs Regular seeds pros and cons
– Marijuana’s butter
– How to extract THC and all its uses
– How to Make Homemade Moroccan Hash
– Buy marijuana seeds
⚠️ Conclusion
You can’t say sativa plants are better than indica ones or the other way around. Each variety has its advantages and disadvantages, but the important thing is that we have many different ones to choose from. Which are your favorites? Tell us in the comments section and if you enjoyed this article we would appreciate it if you share it.😜