- Learn how to build your own indoor grow tent with this guide
- The best indoor growing chart for cannabis


03-10-2024 07:00:45 - Updated: 3 October, 2024
Temperature control is one of the most important factors for achieving successful indoor cannabis cultivation. Inadequate temperature can affect the growth of your plants, decrease yield, and even lead to pests and diseases. Therefore, in this article, we will explain what the ideal temperature for indoor cultivation is for each phase of cannabis growth, how to maintain it stable, and what tools to use to achieve it.
📲 Why is temperature important in indoor cultivation?
Temperature directly influences the metabolism of cannabis plants. A warm environment can accelerate growth, while a cold one slows it down. Additionally, cannabis plants have an optimal temperature range in which they can absorb nutrients more efficiently, perform photosynthesis, and grow healthily.
Maintaining an environment with the right temperature also helps prevent problems such as mold or pest infestations. Very high temperatures can dry out the environment and promote the presence of mites, while low temperatures encourage humidity, which can lead to mold or fungi.
➕ Ideal temperature in different phases of cannabis cultivation
The life cycle of cannabis is divided into several stages: germination, vegetative phase, and flowering. Each of these phases has specific temperature requirements to optimize growth.
1. Germination
During germination, cannabis needs warmer temperatures to encourage seed development. The ideal temperature at this stage is between 20°C and 25°C.
2. Vegetative phase
In the vegetative phase, plants rapidly develop their leaves, stems, and roots. The optimal temperature for this phase varies slightly between day and night:
- Day: between 22°C and 28°C
- Night: between 18°C and 22°C
A warm environment during the day allows plants to grow vigorously, while a slight drop in temperature at night helps them rest and reserve energy for the next day’s photosynthesis.
3. Flowering
The flowering phase is crucial, as this is when the plant develops its buds. Maintaining a stable temperature is essential to maximize resin production and bud quality. Here, temperatures should be slightly lower than in the vegetative phase:
- Day: between 20°C and 26°C
- Night: between 16°C and 20°C
A gradual drop in nighttime temperature during this stage can promote greater trichome production, enhancing the cannabinoid and terpene profile.
🔥 Summary table of the ideal temperature for cannabis cultivation
| Cultivation phase | Day temperature | Night temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Germination | 20°C – 25°C | 20°C – 25°C |
| Vegetative | 22°C – 28°C | 18°C – 22°C |
| Flowering | 20°C – 26°C | 16°C – 20°C |
⭐ How to measure and control the temperature in your indoor cultivation
Controlling the temperature in an indoor cannabis cultivation may seem complicated, but with the right tools and some tips, it is easier than it seems. Here are some recommendations:
1. Thermometers and sensors
It is essential to have several thermometers or sensors in your growing space. Ideally, place at least one at canopy height (the tips of the plants) and another at the bottom to measure the temperature near the substrate.
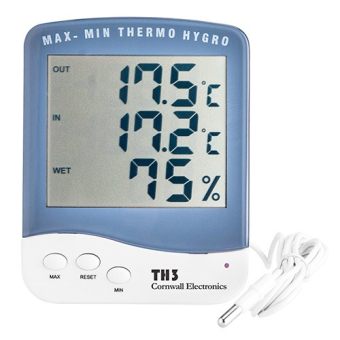
There are thermohygrometers that measure both temperature and humidity, which is useful for controlling both variables simultaneously. Although this article discusses temperature, it is advisable to install at least one digital thermohygrometer with probe to easily check both temperature and humidity without having to access the cultivation area, as the probe can be placed inside, at the height of the upper tips of the plants, and the device left outside to view the readings.
2. Air conditioning and fans
To regulate temperature, ventilation is key. In warm climates or places where temperature is difficult to control, air conditioning can be a fundamental tool. Make sure that air circulates evenly throughout the growing space, using fans to move the hot air that accumulates at the top of the grow room. In grow cabinets, clip-on fans can be attached to the metal structure, and if it is a grow room, wall fans or standing fans can be placed.
3. Air extractor
The air extractor is vital for removing hot air and replacing it with fresh air from outside. This is especially important when using discharge grow lights like HPS, which generate additional heat, but it is also advisable when using LED grow lights, as in addition to controlling temperature, it is essential to renew the air to introduce CO2. Make sure to adjust the extractor speed according to the temperature you want to maintain.
4. Heaters
In cold climates or during the nighttime stages of the flowering phase, a heater may be necessary to prevent the temperature from dropping too low. Make sure the heater has a built-in thermostat to maintain a constant temperature and avoid overheating the environment. Here in Valencia, they are not even necessary in January or February, but in places like northern Germany or the UK, they can be essential tools.
5. Humidifiers and dehumidifiers
Humidity is directly related to temperature. An increase in humidity in the air can cause plants to transpire less, affecting their metabolism. Use a humidifier if the environment is very dry, especially during the first weeks of the plants, or a dehumidifier if humidity is above recommended levels, which is essential during the last weeks of cultivation, from the moment you see the buds starting to form and smell as much as you like.
🥇 Consequences of inadequate temperature
Controlling temperature not only optimizes growth but also prevents potential problems. Here are some consequences of an unadjusted temperature in your cultivation:
- High temperatures (above 30°C): Plants suffer thermal stress, which decreases photosynthetic capacity, dries out faster, and is more prone to pests like mites.
- Low temperatures (below 15°C): Growth slows considerably, and mold or fungi may appear due to the high humidity generated by the cold environment.
- Sharp temperature fluctuations: Extreme changes between day and night can stress the plant, negatively affecting its development and reducing yield.
👾 Cultivation temperature with CO2
When enriching the environment with CO2 in an indoor cultivation, plants can tolerate and benefit from higher than normal temperatures. This is because the increase in CO2 levels allows plants to maintain their transpiration and photosynthesis rates at temperatures that, under normal conditions, would be too high. The optimal temperatures for a CO2-enriched cultivation are:
- Day: between 28°C and 32°C.
- Night: between 18°C and 22°C.
With elevated CO2 levels, plants can handle higher temperatures because they do not dehydrate as quickly. This temperature range maximizes CO2 absorption and increases the photosynthesis rate, accelerating growth. Note! CO2 is applied only during the flowering phase and only during the light cycle.
🎯 Recommended CO2 levels
To make the most of the benefits of CO2, it is essential to maintain levels within an optimal range. The recommended CO2 levels for an enriched indoor cultivation are usually between 1000 and 1500 ppm. Going beyond 1500 ppm does not necessarily improve results and can be counterproductive to plant health. In our own tests, we have obtained good results up to 1800 ppm, but not all strains respond equally well, so we advise not to exceed 1500 ppm.
✅ Relationship between CO2, temperature, and light
One of the most important factors in a CO2 cultivation is ensuring that plants receive enough light. CO2 is only useful when plants have access to intense light that allows them to perform photosynthesis. In high-yield crops, high-intensity LED or HID lights are often used to ensure that plants receive the necessary amount of light.
In addition to light, temperature must be constantly monitored to ensure it is within the appropriate range. If the temperature is too low, CO2 will not be used efficiently, reducing the benefits of its use.
🎲 Summary table of temperature and CO2 in cannabis cultivation
| Cultivation phase | Temperature (day) with CO2 | Temperature (night) | Recommended CO2 levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetative phase | 28°C – 32°C | 18°C – 22°C | 1000 – 1200 ppm |
| Flowering phase | 28°C – 32°C | 18°C – 22°C | 1000 – 1500 ppm |
✨ How to control temperature in a CO2 cultivation
Controlling temperature in a CO2 cultivation requires a proper balance between heat extraction and fresh air introduction. Here are some tips for managing temperature when enriching your cultivation with CO2:
1. Constant monitoring
Using a thermohygrometer (which measures both temperature and humidity) is essential. You should continuously monitor temperatures in different areas of the growing space, especially at the top of the canopy, where the temperature tends to be higher.
2. Adequate ventilation
Although CO2 is beneficial for plants, ventilation remains crucial. An air extractor should run enough to remove excess heat, but not so much as to expel CO2 from the grow cabinet. It is recommended to use a CO2 controller that allows maintaining constant levels within the growing space without losing large amounts of this gas through ventilation.
3. Air conditioning
On the hottest days, especially if you use HID grow lights, you may need air conditioning to keep temperatures below 32°C. Portable air conditioners are a good option for crops in small spaces.
4. LED or CMH lights
Using LED or CMH (ceramic metal halide) lights helps reduce the heat generated in the growing space, making temperature control easier. LED lights, in particular, are much more energy-efficient and generate less heat than traditional HID lights. Right now, there are several LED models for cultivation that offer excellent value for money, which you can easily amortize in a couple of crops, so I highly recommend reading this article dedicated to the best LED grow lights currently available to see the best options.
 |
| Buy LEC 315W Kit |
|---|
5. Uniform CO2 distribution
CO2 tends to accumulate at the bottom of the grow cabinet or room, so it is important to distribute it evenly. This can be achieved by using fans that effectively circulate the air or installing a CO2 diffusion system that ensures uniform coverage.
🧪 Humidity and temperature with CO2
The use of CO2 also impacts humidity levels. An increase in temperature generally comes with an increase in plant transpiration, which raises the relative humidity of the environment. Keeping humidity under control is key to avoiding mold or pest infestations. Here are the recommended humidity levels for a CO2 cultivation:
- Vegetative phase: 50% – 70% relative humidity.
- Flowering phase: 40% – 50% relative humidity.
If humidity is too high, consider using a dehumidifier to keep it within a safe range. CO2 can help increase plant production, but it must be used correctly or it can be negative, and to ensure you have no issues in this regard, I’m sharing this article that perfectly explains how to apply CO2 in indoor cultivation for better results.
🔰 How to lower the temperature of the grow cabinet?
Lowering the temperature in a grow cabinet is crucial to ensure the well-being of your plants, especially if they are developing in a closed environment with little ventilation and powerful lights, which tend to generate heat. Here are several strategies and solutions to efficiently reduce temperature:
1. Improve ventilation
One of the most effective ways to reduce temperature is to improve air circulation within the cabinet. Here are several ways to do this:
- Air extractors: Install a good air extractor that allows you to remove the accumulated hot air inside the cabinet and replace it with fresh air from outside. Make sure the extractor has enough capacity for the size of the cabinet. Extractors with speed control allow you to adjust extraction according to temperature, making them very versatile.
- Oscillating fans: Place fans inside the cabinet to constantly move air between the plants and prevent heat from stagnating at the top. Oscillating fans are ideal because they distribute air evenly throughout the space.
- Fresh air injectors: In addition to the extractor, a fan that introduces fresh air from outside can be very useful. This cold air replaces the expelled hot air and helps maintain controlled temperature.
2. Reduce heat generated by lights
Grow lights are one of the main sources of heat in a grow cabinet. Here are some solutions to reduce their thermal impact:
- Switch to LED lights: High-pressure sodium (HPS) lights and metal halide (MH) lights generate a lot of heat. Switching to LED lights, which are more efficient and emit less heat, can significantly reduce the temperature in the cabinet without compromising light quality. It’s also interesting to switch because with LEDs you achieve higher yield and better quality of the harvest. If you want to know more, don’t miss our article “Indoor cultivation guide with LED”.
- Increase the distance between lights and plants: If lights are too close to plants, they can not only affect temperature but also burn leaves. Adjust the height of the lights to ensure they are at an appropriate distance from the canopy (top of the plants).
- Install a cooling system for the lights (cooltube): A cooltube system can be very effective. This device consists of a tube that surrounds the bulb, allowing an extractor to remove the heat generated by the light directly outside the cabinet without heating the growing space.
3. Portable air conditioning
If your grow cabinet is in a room that tends to heat up a lot, using a portable air conditioner can be an effective solution. Make sure to choose equipment suitable for the size of the room or cabinet. Air conditioning helps maintain a constant temperature, but keep in mind that it may increase energy consumption.
4. Thermal insulation
Ensure that the grow cabinet is well insulated thermally so that external heat does not affect the interior as much. Rooms with poorly insulated walls or large windows can heat up much faster. Using reflective materials inside the cabinet, such as mylar, helps keep light inside and prevents walls from absorbing unnecessary heat.
5. Control the light cycle
If the ambient temperature of the room where the grow cabinet is located is lower at night, you can schedule the light cycle of the plants to be on during nighttime and off during the day, when the environment is warmer. Here are a few electric timers that will allow you to schedule the light cycle as you wish.
6. Use inline air extractors with carbon filter
These extractors not only help remove hot air but also filter odors. An inline ventilation system, which can be integrated with the extractor and an anti-odor carbon filter, extracts hot air while purifying the circulating air, helping to maintain a controlled temperature. To know the power of the extractors you need to install in your cultivation, here’s an article titled “How to calculate air extraction and intake in indoor cultivation”.
7. Evaporative coolers
An evaporative cooler (also called “swamp cooler”) is an efficient option in dry places. This device uses water to cool the air before introducing it into the growing space. However, be careful with the increase in humidity it may generate, as excess humidity can promote the appearance of mold and pests.
8. Space optimization
Distribute plants correctly: Do not overcrowd the growing space, as an overly full space will reduce air circulation and retain heat. Leave enough space between plants for air to flow freely.
Place the cabinet in a cool location: If possible, locate your grow cabinet in a cooler room or basement of the house, away from direct sunlight or heat-generating appliances.
9. Automated temperature control systems
Investing in an automatic temperature controller can help you maintain the perfect environment without constantly worrying. These devices regulate the on and off of extractors, fans, and heaters according to the set temperature.
10. Humidity and its relationship with temperature
Controlling relative humidity can influence temperature. Often, lowering temperature also requires lowering humidity. If the air in your cabinet is too humid, consider using a dehumidifier to extract excess humidity, which can also lower temperature. Remember that the appropriate humidity should be between 40% and 60%, depending on the stage of cultivation. If you want to delve deeper into this, don’t miss this article that explains how to lower humidity in indoor cultivation easily.
🦋 Editor’s opinion
Experience in indoor cannabis cultivation has shown me that temperature management is one of the most underestimated factors, but also one of the most decisive. A small adjustment in temperature control, especially during the flowering stage, can make the difference between good quality buds and a mediocre harvest. I always recommend being attentive to the climatic conditions of the grow room and adjusting equipment according to the needs of the plants.
Have you ever wondered why plants can withstand over 40 ºC outdoors but not in indoor cultivation? This is because in indoor cultivation, plants easily become stressed as they are not in their natural environment, while outdoors they are more resilient due to the sun, continuous exposure to CO2-rich air, and usually have more space for the root system. Other blogs won’t tell you this, because Pevgrow keeps no secrets to ensure its readers and friends always achieve the best possible harvest.
🌱 FAQs
What is the maximum temperature for indoor cultivation?
The maximum recommended temperature for indoor cultivation is 30°C, as above this temperature plants may experience thermal stress, slowing their growth and affecting nutrient absorption.
What is the ideal temperature and humidity for indoor cultivation?
The ideal temperature during the day ranges between 22°C and 28°C, and relative humidity should be between 40% and 60%, depending on the growth phase. During flowering, it is advisable to keep humidity at a lower level, between 40% and 50%.
How do high temperatures affect crops?
High temperatures, above 30°C, can cause plants to enter thermal stress, reducing their photosynthesis capacity, which decreases growth and may increase vulnerability to pests and diseases.
What is the ideal temperature in a cultivation with LED?
In a cultivation with LED lights, the ideal temperature is between 24°C and 26°C, as LED lights generate less heat than other types of lighting, allowing for a slightly cooler environment.
What is the minimum temperature in an indoor cultivation?
The minimum temperature for indoor cultivation should be kept above 15°C. Lower temperatures can slow plant growth and increase the risk of problems such as mold or fungi.


















Excellent article! It helped me clarify all my doubts about the ideal temperature for indoor cultivation and how to maintain an optimal environment for my plants.